soft agar colony formation assay golden test for malignant transformation|carmofur in clonogenic survival assays : purchasing The anchorage-independent soft-agar colony formation assay has been widely used as a bridge between adherent cell cultures and animal tumor studies, providing a reliable . ВКонтакте — крупнейшая социальная сеть в России и стр.
{plog:ftitle_list}
WEBLinktree. Make your link do more.
In this study, we established two in vitro transformation assays, the soft agar colony-forming assay (SACF) and the growth in low attachment . The soft agar colony formation assay is a well-established method for characterizing this capability in vitro and is considered to be one of the most stringent tests .The digital soft agar colony formation (D-SAC) assay is an ultrasensitive in vitro test for detecting tumorigenic transformed cells in hCTPs. Methods: In this study, we first evaluated the colony formation efficiency (CFE) precision of . The soft agar colony formation (SACF) assay, which is a well-known in vitro assay for the detection of malignant transformed cells, is .
The anchorage-independent soft-agar colony formation assay has been widely used as a bridge between adherent cell cultures and animal tumor studies, providing a reliable .The digital soft agar colony forma-tion (D-SAC) assay is an ultrasensitive in vitro test for detecting tumorigenic transformed cells in hCTPs.
The soft agar colony formation (SACF) assay, which is a well-known in vitro assay for the detection of malignant transformed cells, is applicable for the quality assessment of hCTPs. The soft agar colony formation (SACF) assay is a method for monitoring anchorage-independent cell growth, which is characteristic of malignant transformed cells and has been widely used in vitro for detecting tumorigenic transformed cells [11, 12].We have previously confirmed that transformed cell lines can proliferate and form a single colony from .
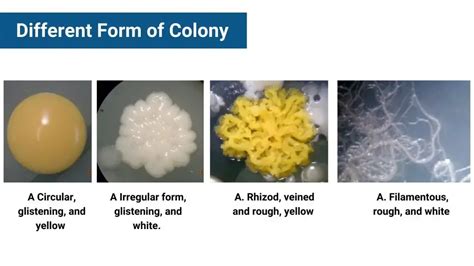
Anchorage-independent growth is the ability of transformed cells to grow independently of a solid surface, and is a hallmark of carcinogenesis. The soft agar colony formation assay is a well-established method for characterizing this capability in vitro and is considered to be one of the most stringent tests for malignant transformation in cells. This . In order to test whether cells have been malignantly transformed, the soft agar colony formation assay, first described almost 50 years ago, can be performed. The results obtained with this assay have consistently been shown to . A soft agar colony formation assay on H1299 cells with either wild type METTL3 protein or METTL3 with a mutation that turns four key lysine residues to arginine residues to prevent SUMOylation. Relevant section of caption for published figure reads: “(A) The mutation of 4KR in METTL3 reduces the soft-agar colony formation of H1299 cells .
Background aims: The administration of human cell-processed therapeutic products (hCTPs) is associated with a risk of tumorigenesis due to the transformed cellular contaminants. To mitigate this risk, these impurities should be detected using sensitive and validated assays. The digital soft agar colony formation (D-SAC) assay is an ultrasensitive in vitro test for detecting .The Soft Agar Assay for Colony Formation is an anchorage independent growth assay in soft agar, which is considered the most stringent assay for detecting malignant transformation of cells. For this assay, cells (pretreated with carcinogens or carcinogen inhibitors) are cultured with appropriate controls in soft agar medium for 21-28 days.The Soft Agar Assay for Colony Formation is an anchorage independent growth assay in soft agar, which is considered the most stringent assay for detecting malignant transformation of cells. For this assay, cells (pretreated with carcinogens or carcinogen inhibitors) are cultured with appropriate controls in soft agar medium for 21-28 days.
A soft agar colony formation assay on H1299 cells with either wild type METTL3 protein or METTL3 with a mutation that turns four key lysine residues to arginine residues to prevent SUMOylation. Relevant section of caption for published figure reads: “(A) The mutation of 4KR in METTL3 reduces the soft-agar colony formation of H1299 cells . Indeed, soft agar colony formation assay is one of the most rigorous assays available to assess cell invasion . While similar high-throughput assays have been optimised for other cancer cells, this has not been the case for medulloblastoma, a cancer that shows a high level of metastasis [ 8 ], and lacks optimised 3D high-throughput assays for .
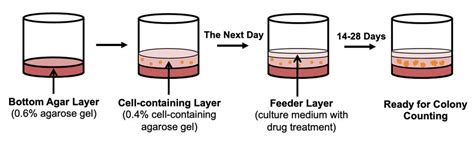
Our CytoSelect™ 96-Well Cell Transformation Assay (Soft Agar Colony Formation) is suitable for measuring cell transformation where no downstream analysis is required. Cells are incubated in a semisolid agar medium for 7-8 days. The cells are then solubilized, lysed and detected using the included fluorescent dye in a fluorometric plate reader.. Cells incubated using this assay .
The soft agar colony formation (SACF) assay, which is a well-known in vitro assay for the detection of malignant transformed cells, is applicable for the quality assessment of hCTPs. Here we established an image-based screening system for the SACF assay using a high-content cell analyzer termed the digital SACF assay.Traditionally, the soft agar colony formation assay is a common method to monitor anchorage-independent growth, which measures proliferation in a semisolid culture media after 3-4 weeks by manual counting of colonies. Standard soft agar assays . Here, we investigated the role of miR-301a during arsenic-induced cellular transformation and tumor formation. miR-301a was found to be upregulated during arsenic-induced BEAS-2B transformation .
what forms soft uniform colonies
A soft agar colony formation assay on H1299 cells with either wild type METTL3 protein or METTL3 with a mutation that turns four key lysine residues to arginine residues to prevent SUMOylation. Relevant section of caption for published figure reads: “( A ) The mutation of 4KR in METTL3 reduces the soft-agar colony formation of H1299 cells.
Soft Agar Colony Formation Assay Anchorage-independent Growth Carcinogenesis In Vitro Transformation Wnt7A Frizzled-9 Murine Lung Carcinoma Tumor Suppression Read Article Cite this ArticleThe soft agar colony formation assay is a well-established method for characterizing this capability in vitro and is considered to be one of the most stringent tests for malignant transformation in cells. This assay also allows . Colony formation on soft agar was assayed in triplicate by plating 5000 transfected cells in a layer of 0.3% (w/v) agar in an assay of supplemented DMEM for HCT116/HT29 and RPMI medium for MCF-7 .
Soft agar colony formation assay is a well-established method to evaluate cellular anchorage-independent growth for the detection of the tumorigenic potential of malignant cells (Roberts et al., 1985), which is developed from plate colony formation assay described by Puck et al. in 1956 where cells were seeded on to a culture plate to assay the .
The soft agar colony formation assay is a test to determine whether cells are anchorage-independent. Anchorage independence is a characteristic of cells that have undergone malignant transformation. Also known as. Test of anchorage independence . A soft agar colony formation assay on H1299 cells with either wild type METTL3 protein or METTL3 .The Soft Agar Assay for Colony Formation is an anchorage independent growth assay in soft agar, which is considered the most stringent assay for detecting malignant transformation of cells. For this assay, cells (pretreated with carcinogens or carcinogen inhibitors) are cultured with appropriate controls in soft agar medium for 21-28 days. The soft agar colony formation assay serves as one of the hallmarks of carcinogenesis 43 and has been shown to be dependent on FN. 44 Hence, we monitored the ability of these breast cancer cells . Figure 1.CS-induced malignant transformation in BEAS-2B cells in vitro and in vivo.(A) Representative photographs of the colony formation assay of the normal BEAS-2B cells and S30 cells.(B) Graph of soft agar colony forming rate of normal BEAS-2B cells and S30 cells. **p < 0.01 vs. BEAS-2B.(C) Photographs of tumors excised 45 days after injection of normal .
Background. Anchorage-independent growth is an ability of cells to grow independently on a solid surface, and is considered as a hallmark of carcinogenesis (de Larco and Todaro, 1978).Soft agar colony formation assay is a well-established method to evaluate cellular anchorage-independent growth for the detection of the tumorigenic potential of . Soft agar colony growth from transformed control and Casp3 KO HFF (D) and BJ1 (E) cells. Data are presented as mean ± SD, n = 3. p values were determined using Student’s t -test.
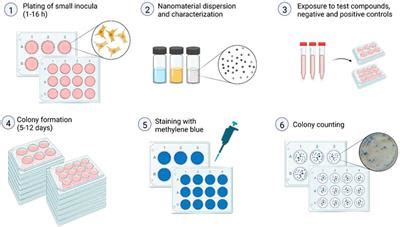
Traditionally, the soft agar colony formation assay is a common method to monitor anchorage-independent growth, which measures proliferation in a semisolid culture media after 3-4 weeks by manual counting of colonies. Standard soft agar assays .
The soft agar colony formation (SACF) assay is a method for monitoring anchorage-independent cell growth, which is characteristic of malignant transformed cells and has been widely used in vitro for detecting tumorigenic transformed cells [11,12].We have previously confirmed that transformed cell lines can proliferate and form a single colony from a single cell .
soft agar assay protocol
Reclame Aqui: vestcasa.com.br. Cuidado. Segundo o Reclame Aqui, o site vestcasa.com.br não entrega uma boa experiência de compra ou serviço. A reputação .
soft agar colony formation assay golden test for malignant transformation|carmofur in clonogenic survival assays